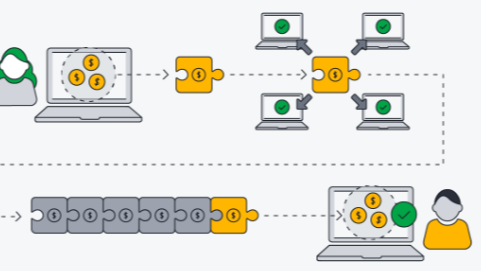
Blockchain technology functions as a decentralized ledger system, enabling secure transaction recording across numerous computers. Its design incorporates key components such as cryptographic algorithms and consensus mechanisms, which ensure data integrity. The process of validating transactions involves complex calculations and various methodologies. Understanding the intricacies of these elements reveals not only how blockchain operates but also its potential implications in different sectors. What follows provides a deeper insight into these transformative applications.
What Is Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain technology is a decentralized digital ledger system that enables secure and transparent record-keeping across a network of computers.
This innovation ensures immutable records, preventing unauthorized modifications and enhancing data integrity.
By distributing control among participants, blockchain empowers individuals with enhanced freedom, reducing reliance on centralized authorities.
Its design fosters trust and accountability, making it an ideal solution for various applications in diverse sectors.
Key Components of Blockchain
At the core of blockchain technology lie several key components that facilitate its operation and functionality.
The decentralized ledger ensures transparency and immutability, enabling multiple parties to maintain a unified record without central authority.
Additionally, cryptographic security safeguards data integrity, preventing unauthorized access and tampering.
Together, these components empower users, fostering a trustless environment conducive to innovation and freedom in digital transactions.
How Transactions Are Processed
The processing of transactions within a blockchain network relies on a series of systematic steps designed to ensure accuracy, security, and consensus among participants.
Initially, transaction validation occurs, where nodes verify the authenticity of transactions.
Subsequently, consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Work or Proof of Stake, are employed to achieve agreement across the network, ensuring that only legitimate transactions are recorded in the blockchain.
Applications of Blockchain in Various Industries
As industries continue to seek innovative solutions to enhance efficiency and transparency, the adoption of blockchain technology has gained momentum across various sectors.
In finance, blockchain provides secure, decentralized finance solutions that streamline transactions and reduce fraud.
Additionally, in the supply chain sector, blockchain enhances traceability and accountability, ensuring that all parties have access to real-time data, thereby optimizing operations and reducing costs.
Conclusion
In summary, blockchain technology serves as a robust framework for decentralized transactions, ensuring security and transparency through its innovative structure. By harnessing cryptographic algorithms and consensus mechanisms, it mitigates the risks of unauthorized access and data manipulation. As industries continue to explore its potential, blockchain stands poised to revolutionize traditional processes, creating a world where trust is built not on authority but on technology. Ultimately, it is a game-changer that could tip the scales towards greater efficiency and accountability.